Key Takeaways
1. Traditional attribution is broken: AI assistants now influence 20–50% of purchase decisions without leaving measurable traces in Google Analytics, creating a major blind spot for brands.
2. Mint’s 5-step framework: A structured methodology to master AI search, from fixing attribution to executing a concrete optimization roadmap.
3. The new essential metrics: Visibility (brand mentions), sentiment (AI-generated score), and alignment (accuracy of positioning) are replacing traditional SEO KPIs.
Why Do Brands Need to Rethink Their Search Strategy with AI?
The Limits of Google Analytics in the Face of AI Assistants
The Rise of a New Discovery Ecosystem
Why AI Doesn’t Click Like a Human: New Attribution Rules
The Mint AI Search Framework: A Structured 5-Step Approach
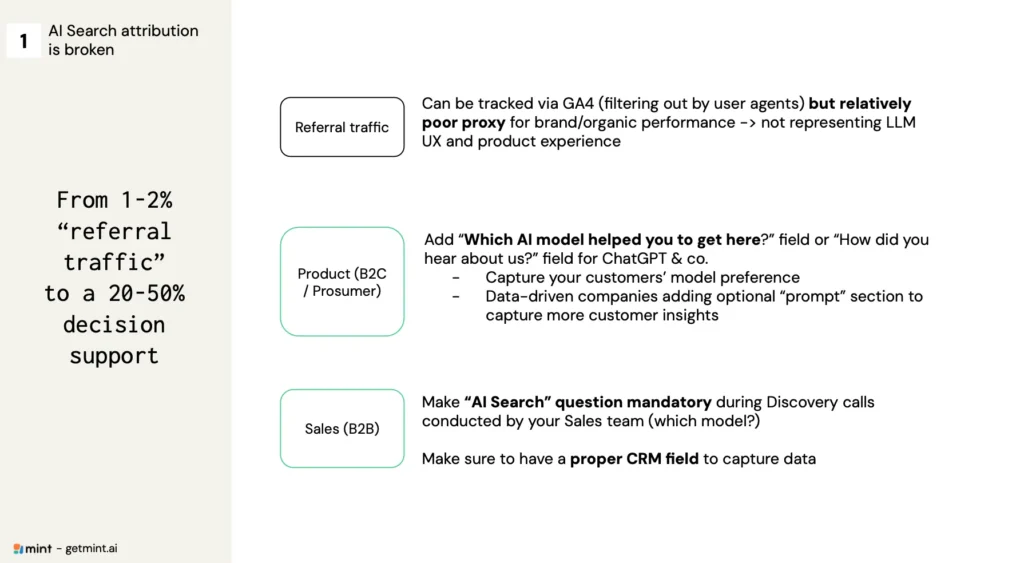
Step 1: Fix Attribution and Capture AI Signals
The first step is to implement explicit capture mechanisms. For product teams, this means enriching existing forms (e.g., “How did you hear about us?”) by adding AI models (ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, etc.) as response options. B2B teams should integrate these questions into their CRM to track AI influence on the sales pipeline.
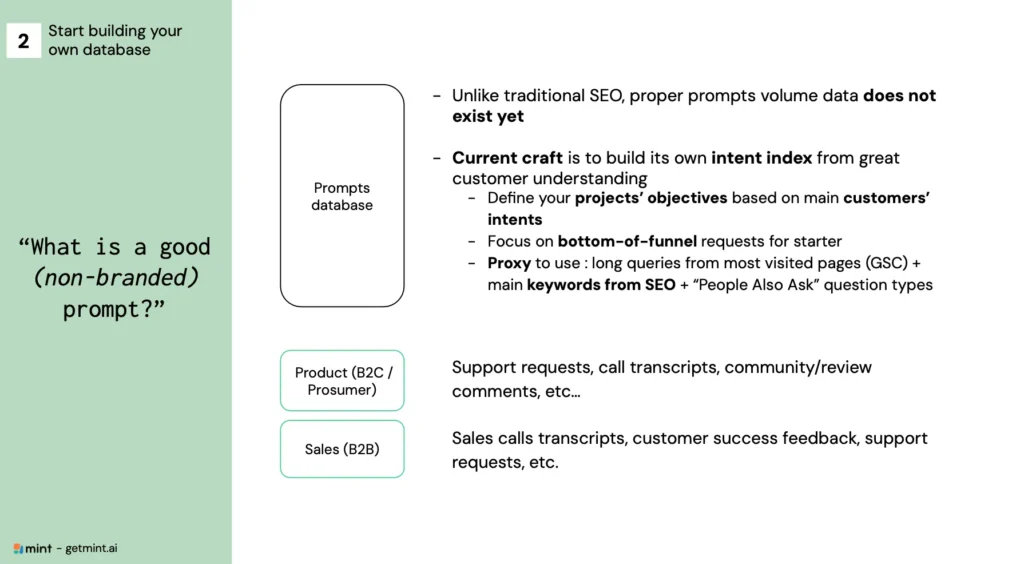
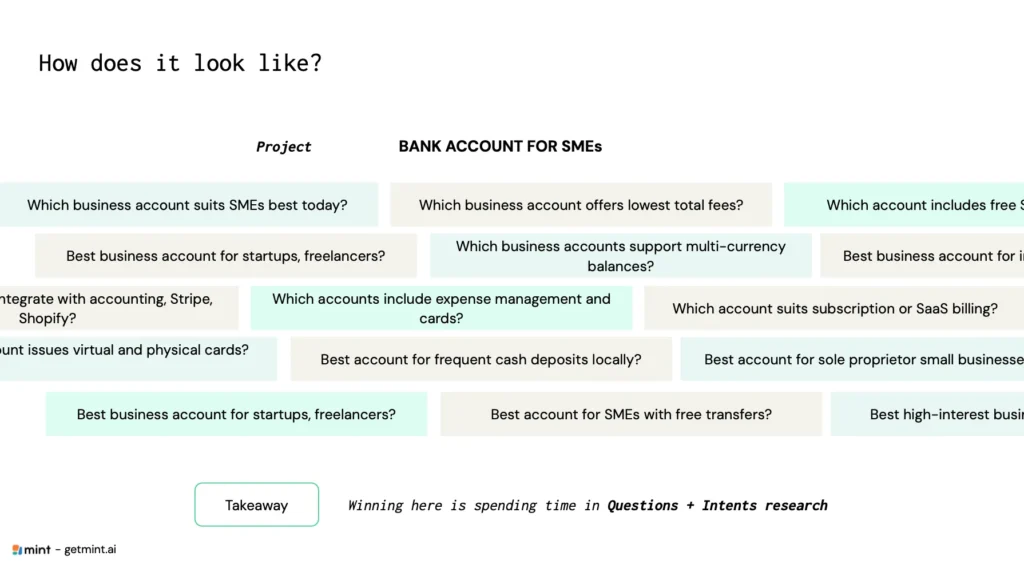
Step 2: Build Your AI Intent Database
Step 3: Redefine Your KPIs for the AI Era
- Visibility (frequency of mentions),
- Sentiment (tone of recommendations),
- Alignment (accuracy of positioning).
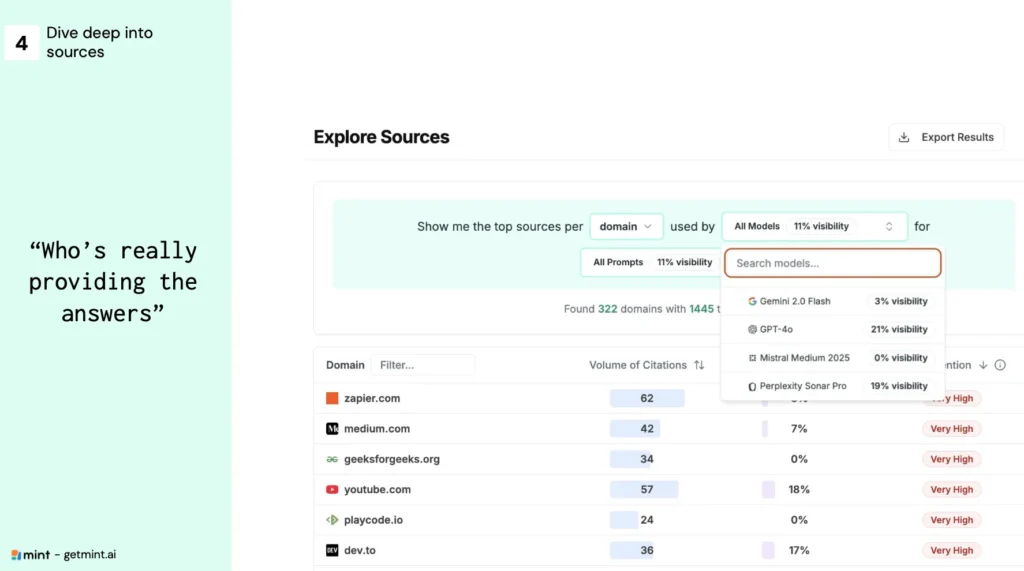
Step 4 — Analyze and Prioritize the Sources Consulted by AIs
Step 5 — Take Action: Define a Pragmatic and Prioritized Roadmap
- influence external sources,
- refresh existing content,
- create unique assets.
How Do AI Answer Engines Actually Work?
The Technical Process: From Query to Synthesis
The Different Modes of Information Retrieval
The Crucial Importance of Sources and Citations
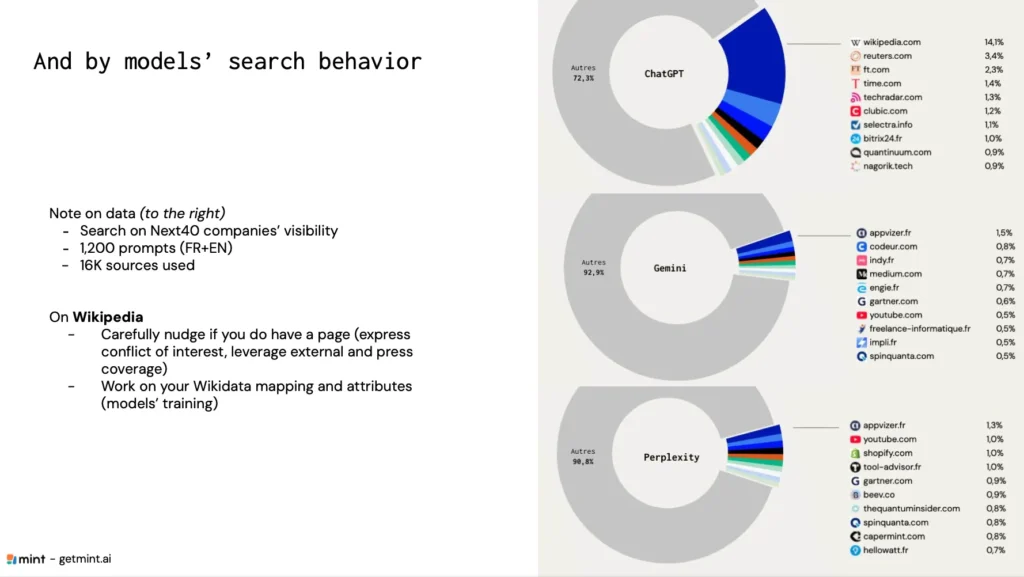
Which Sources Most Influence AI Answers?
The Analysis of 16,000 Sources: ChatGPT vs Gemini vs Perplexity
Wikipedia & Wikidata Cases: Opportunities and Constraints
Reddit Case: Massive US Adoption, Emerging in Europe
The Importance of External Sources
Differences by Language, Market, and Question Type
The Three-Pillar Optimization Strategy
Influence: Gain Positive Off-Site Mentions
Refresh: Adapt Your Existing Content for AI
Create to Own: Produce Unique and Citable Assets
How to Structure Your Content to Maximize AI Visibility?
The 5 Essential Page Structure Pillars
The Importance of Conversational Language and Direct Answers
Adding Differentiated Value: Data, Studies, Unique Insights
The Role of Schema Markup and Structured Data
Watch the GetMint Webinar Replay and Access the Presentation
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, but not with Google Analytics alone. AI referral shows only 1–2% of traffic, while real influence is 20–50%. The key is to explicitly capture signals: fields in your forms (“Did you use an AI model?”), questions asked on calls, dedicated CRM fields. Mint then automates the tracking of these signals.
- Traditional SEO: optimize for clicks and Google ranking.
- AEO (Answer Engine Optimization): optimize to be mentioned, cited, and accurately described in AI answers.
- Visibility: is your brand mentioned? How often?
- Sentiment: are the answers positive, neutral, or negative?
- Alignment: does the wording correctly reflect your values and differentiators?
- ChatGPT: often academic + Wikipedia.
- Gemini: strongly tied to the Google ecosystem.
- Perplexity: more diversified.
Yes, where possible. Wikipedia remains a major source for all models, but rules must be respected (declared conflict of interest, reliable third-party sources). Wikidata, easier to enrich, is widely used in LLM training phases.
- Influence: get positive mentions in relevant third-party sources (PR, partnerships, UGC).
- Refresh: update existing content to make it “AI-ready” (FAQ, clarity, freshness).
- Create to Own: produce unique content (studies, proprietary data, exclusive insights).
- clear, fast structure, accessible HTML,
- fresh, conversational content,
- direct answers to questions,
- structured data (schema markup).
robots.txt, models almost never read LLM.txt. Better to focus on:- the readability of your pages (HTML vs heavy JavaScript),
- content accessibility,
- quality and freshness of information.